What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease, which causes digestive tract inflammation and leads to abdominal pain, severe diarrhea and other issues. The inflammation can also spread into deeper layers of the bowel. The disease primarily involves the intestinal system, but it also has a variety of other manifestations and can affect the skin, joints, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. It starts typically in childhood or through early adulthood, but can develop at any age. Crohn's disease is painful, debilitating, and sometimes may lead to life-threatening complications.
Types of Crohn’s Disease
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease vary from person to person. There are majorly five types of Crohn’s disease, with its own set of symptoms. The type can be defined by the location of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ileocolitis
- Ileitis
- Gastroduodenal Crohn's Disease
- Jejunoileitis
- Crohn's (Granulomatous) Colitis
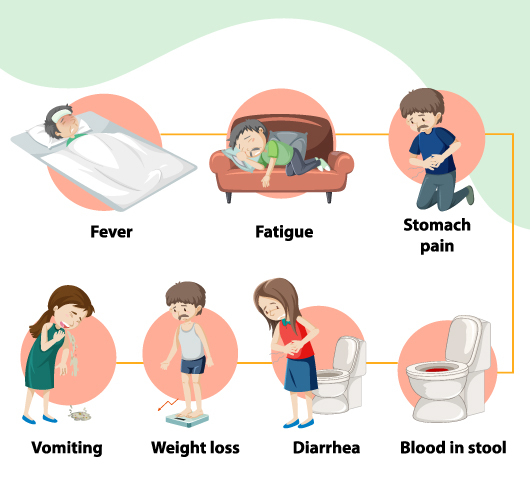
Crohn’s Disease Symptoms
The symptoms of Crohn's disease can vary, depending where and how severe the inflammation is. The most common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Mouth Ulcer
- Blood in your stool
- Reduced appetite
- Irregular Menstruation
- Weight loss
- Inflammation of skin, eyes and joints
- Kidney stones
- Anemia (Iron Deficiency)
- Blood in stool
- Nausea and vomiting
Crohn’s Disease Other Complication
- Bowel Obstruction
- Ulcers
- Fistulas
- Anal Fissure
- Malnutrition
- Colon Cancer
- Blood clots

Crohn’s Disease Causes
Anyone can be affected by Crohn's disease, irrespective of ethnic background. It is more common in Caucasians, though the rates of Crohn’s disease have increased among Hispanics and Asians in recent years.
- Poor Immune System
- Diet & Stress
- Hereditary & Genetic
- Smoking
- Certain Medication
- Environmental Factors
Crohn’s Disease Diagnosis
There is no single test to confirm Crohn’s diagnosis and the symptoms are much similar to other conditions, like bacterial infection.
- Blood Test
- Stool Test
- Endoscopy
- Chromoendoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- CT Scan
- MRI Scan
- Biopsy

Crohn’s Disease Treatment
The treatment plan varies from simply using altering the diet or nutrition and medication. At severe extent, the patient undergoes surgical procedures to repair or remove the affected GI tract portion.

Medications
- Antidiarrheal
- Anti-inflammatory (Oral 5-Aminosalicylates & Corticosteroids)
- Immunomodulators
- Antibiotics
Surgery
- Ostomy
- Ileostomy
- Colostomy
- Colectomy
- Proctocolectomy
- Strictureplasty
Risk of Surgery
- Infection
- Malabsorption
- Marginal Ulcers
- Pouchitis
- Strictures
Natural Treatments for Crohn’s Disease
- The body is self healing
- Fruits like bananas, papayas, mangoes, melons, apples, pears, blended into smoothies or juiced are great for Crohn’s patients
- Vegetables like potatoes, sweet potato, yams, squash, zucchini, broccoli, are also great for Crohn’s patients
- The food we eat gives the body the rights conditions to heal.
Crohn’s disease cannot be cured by medication. Medications are used to slow down the disease progression. The medications do not provide an effective cure, they tend to subdue the symptoms and as a result the patient will need to undergo surgery when the condition worsens. This is why High Carb Health recommends allowing the body to heal naturally via changes in diet and lifestyle to address the root cause of the disease.
To heal, we must allow the body’s defense system to do its job and remove the toxic matter. This means providing the body with the correct conditions so that healing can take place. Only when the body is given the right conditions, via a healthy diet consisting of mostly raw fruits and vegetables, proper hydration, and rest, will the body heal naturally.


